How to Grow Salvia Seeds
Grow Guide #2316
Family: Lamiaceae
Binomial name: Salvia sp.
Life Cycle: Perennial (sometimes grown as an annual)
This 'How to Grow' guide details everything a home gardener needs to know to plant, grow and care for Salvia (Salvia sp.).
When to Sow Salvia Seeds
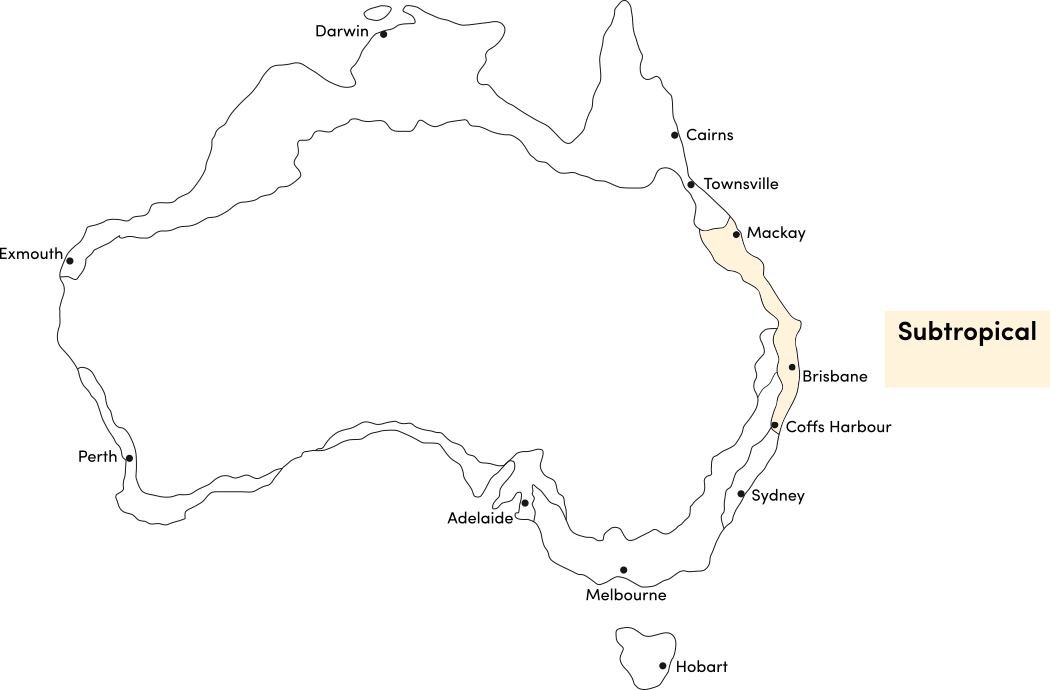
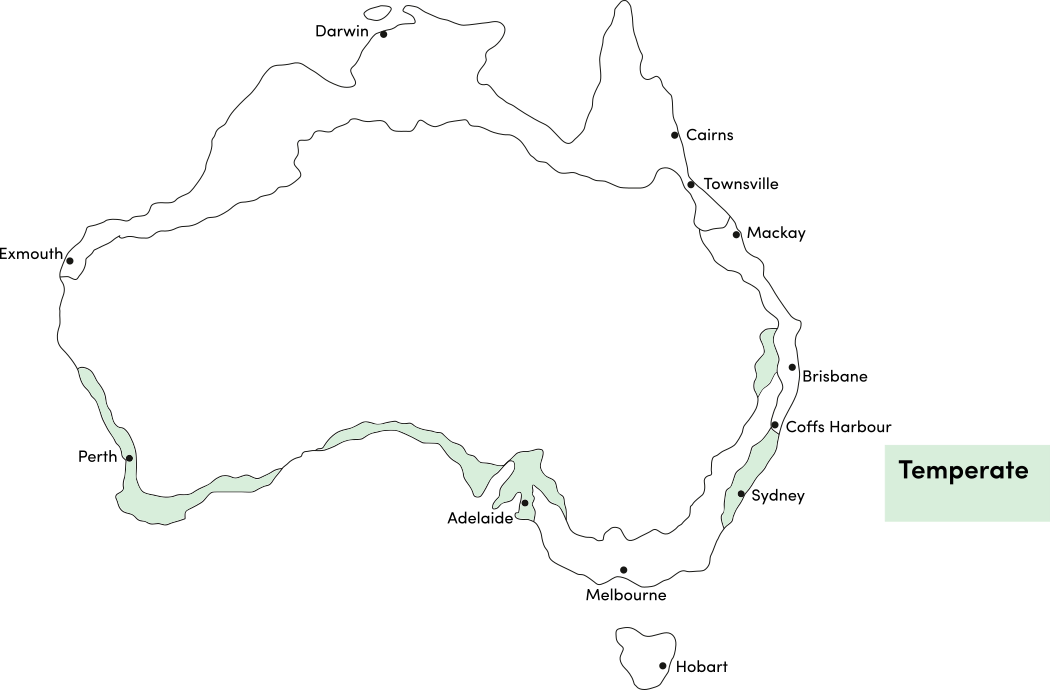
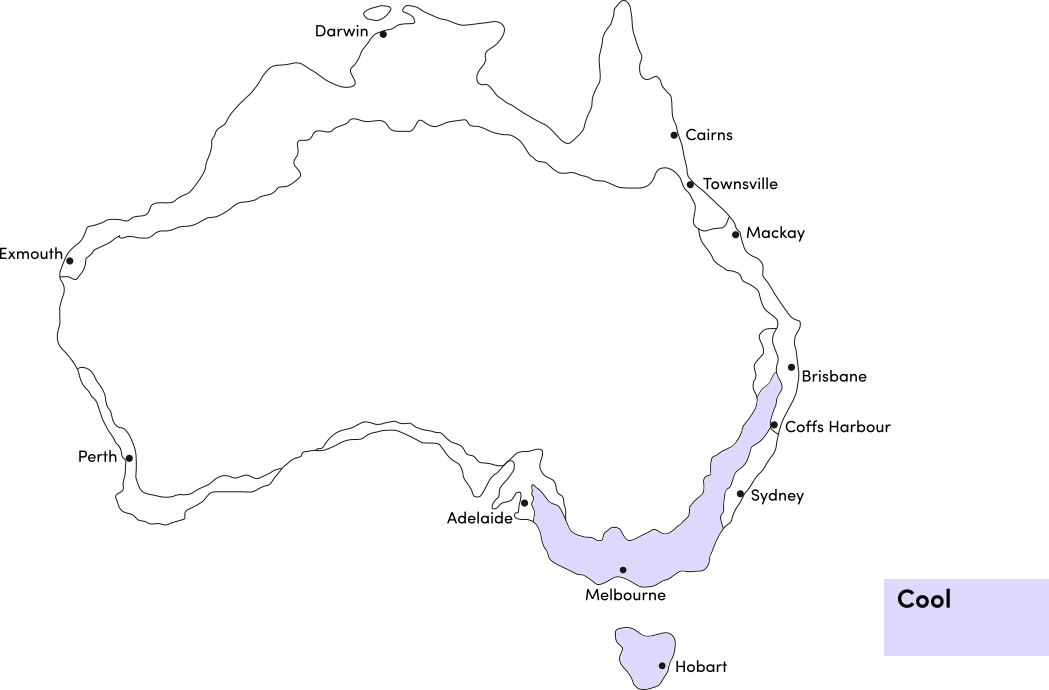
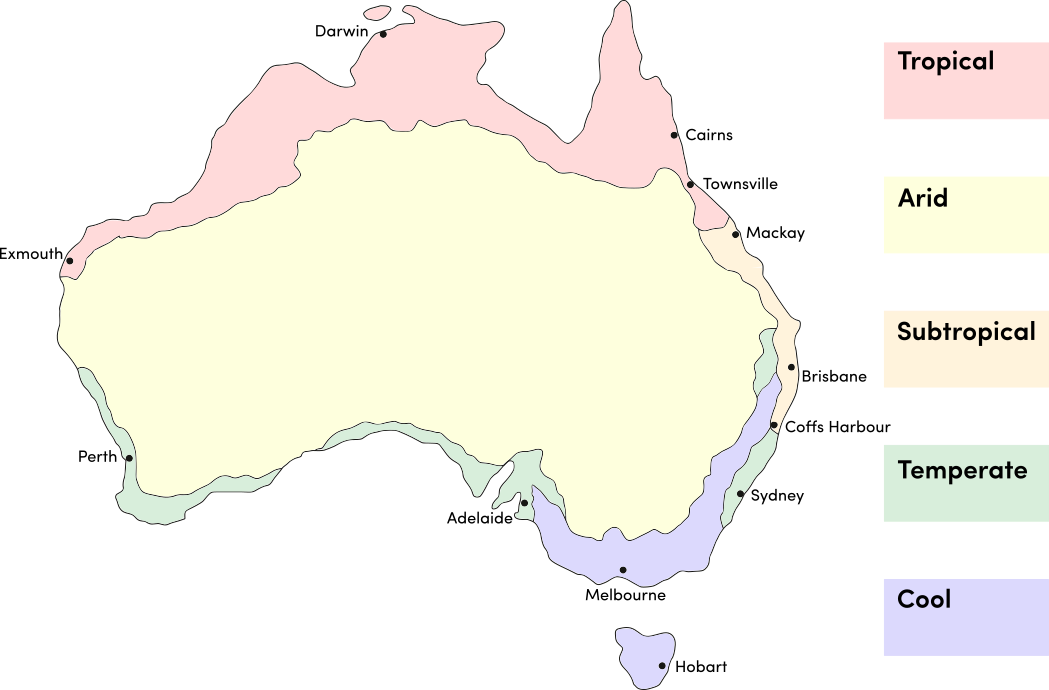
Salvias can be warm-season annuals or perennials that grow year round in most climates. Use the table below to identify the best time of year to sow salvia seeds in your climate.
| JAN | FEB | MAR | APR | MAY | JUN | JUL | AUG | SEP | OCT | NOV | DEC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cool | ||||||||||||
| Temperate | ||||||||||||
| Sub-Tropical | ||||||||||||
| Tropical | ||||||||||||
| Arid |
Preparation
Salvia plants are best grown in full sun. Choose a location that will receive at least 6 hours of full sun each day.
Some salvia plants are perennial, meaning they live for several years. If you are growing a perennial variety, choose a permanent position where plants can grow undisturbed by regular digging or disturbance.
Salvia plants need a well drained soil enriched with plenty of organic matter. Prepare soil by weeding it thoroughly, digging it over to loosen it and adding aged animal manure or compost. Keep the area free of weeds until planting. Learn more about preparing soil for planting here.
Salvia plants can be grown in containers. If possible choose a variety that’s recommended for container growing. Use a good quality potting mix and make sure your container is large enough for mature plants; a minimum of 10 litres is recommended for salvia. During the growing season, keep in mind that container grown plants may need additional fertiliser to encourage healthy growth.
How to Sow Salvia Seeds
Salvia seeds do not require any treatment (eg soaking, stratification) before sowing.
Salvia seeds can be sown directly into the garden OR seedlings can be raised in trays or other containers and transplanted to the garden once established.
Sow Direct
- Sow seeds directly in the garden 4mm deep and 30cm apart.
- Keep soil moist but never wet or dry.
- Seeds should germinate in around 12-15 days at a soil temperature of 22-24°C.
- Young seedlings will need protection from pests, pets and weather until they are established.
Raise Seedlings
- Fill trays, punnets or jiffy pots with a good quality seed-raising mix, or use soil starter pellets.
- Sow seeds 4mm deep.
- Keep soil moist but never wet or dry.
- Seeds should germinate in around 12-15 days at a soil temperature of 22-24°C.
- Transplant seedlings to the garden once they have their first true leaves and are large enough to handle (usually 5-10cm tall).
- Plant out, spacing plants 30cm apart.
Optional: In cool climates salvia seeds can be sown indoors 6 weeks before the last expected frost. Grow them in a warm position with plenty of natural light.
How to Grow Salvia
Salvia plants are drought tolerant once established and grow best in soil that is dry and very well drained. Let the soil dry out between watering, and only water when the soil is dry about 10cm below the surface (test this by scratching away a little soil with your finger), even in summer. Water deeply in the early morning or late afternoon. Avoid watering the leaves of plants to avoid fungal diseases. Learn more about watering here.
If soil was well prepared no extra fertiliser should be necessary. In poor soil or to give your plants an extra boost, application of a high-potassium fertiliser or one formulated for flowering plants can be beneficial:
- Apply slow release fertiliser at the recommended rate when transplanting or when seedlings are 5-10cm tall.
- Apply liquid fertiliser at the recommended rate and frequency while plants are fruiting or flowering.
Optional: Pinch out the growing tips of salvia plants to encourage denser growth with stronger stems and more flowers. Using sharp secateurs or snips remove the top set of leaves, cutting just above a set of lower leaves.
Salvia plants should flower in approximately 75 days.
Optional: When plants have finished flowering prune them back to neaten them and encourage strong new growth. Using sharp secateurs or snips, cut individual stems just above a set of lower leaves.
Common Problems when Growing Salvia
Like all plants, salvia is susceptible to some pests, diseases and other problems. Below is a list of the most common problems gardeners encounter when growing salvia plants:
 Aphids are small (2-4mm long) sap-sucking insects that congregate on the new shoots or the undersides of leaves. They can cause leaves to wilt or become discoloured, and also excrete honeydew which can attract ants and other insect pests. To manage aphids, remove them by spraying with a garden hose, apply a soap or alcohol spray, or encourage predatory insects to your garden. Read more about aphids here.
Aphids are small (2-4mm long) sap-sucking insects that congregate on the new shoots or the undersides of leaves. They can cause leaves to wilt or become discoloured, and also excrete honeydew which can attract ants and other insect pests. To manage aphids, remove them by spraying with a garden hose, apply a soap or alcohol spray, or encourage predatory insects to your garden. Read more about aphids here..jpg) Powdery mildew is caused by fungal spores reproducing on the leaves of plants. First showing as white spots on leaves, affected areas can spread quickly to cover the entire leaf surface. While rarely fatal, powdery mildew can reduce yields. Water plants at soil level (not on leaves) to prevent spreading spores, allow good air flow between plants, remove affected leaves and if necessary spray with an appropriate fungicide or homemade spray. Read more here about powdery mildew here.
Powdery mildew is caused by fungal spores reproducing on the leaves of plants. First showing as white spots on leaves, affected areas can spread quickly to cover the entire leaf surface. While rarely fatal, powdery mildew can reduce yields. Water plants at soil level (not on leaves) to prevent spreading spores, allow good air flow between plants, remove affected leaves and if necessary spray with an appropriate fungicide or homemade spray. Read more here about powdery mildew here. Slugs and snails are molluscs that feed on tender leaves and shoots, mostly at night, leaving slimy trails behind them. Control them by removing their hiding places, keeping free range poultry, collecting them by torchlight or by placing traps. Read more about slugs and snails here.
Slugs and snails are molluscs that feed on tender leaves and shoots, mostly at night, leaving slimy trails behind them. Control them by removing their hiding places, keeping free range poultry, collecting them by torchlight or by placing traps. Read more about slugs and snails here. Spider mites (Tetranychus urticae), also known as two spotted mites, are sap-sucking arachnids that cause dry, wilted or discoloured leaves. The undersides of leaves may feel dry and a little like fine sandpaper. Prune plants to allow good air flow or spray with eco-oil or wettable sulphur. Learn more about managing spider mites here.
Spider mites (Tetranychus urticae), also known as two spotted mites, are sap-sucking arachnids that cause dry, wilted or discoloured leaves. The undersides of leaves may feel dry and a little like fine sandpaper. Prune plants to allow good air flow or spray with eco-oil or wettable sulphur. Learn more about managing spider mites here. Thrips are black, beige or white flying insects (<1.5mm) with larvae that suck tissue from leaves and petals, leaving behind very small white or transparent markings. While not usually causing serious damage, the marks affect the look of flowers and foliage and thrips can also transfer pathogens from one plant to another. Wash thrips from affected plants using a garden hose, encourage predatory mites and lacewings with companion planting, or spray with soap, eco-oil or neem oil.
Thrips are black, beige or white flying insects (<1.5mm) with larvae that suck tissue from leaves and petals, leaving behind very small white or transparent markings. While not usually causing serious damage, the marks affect the look of flowers and foliage and thrips can also transfer pathogens from one plant to another. Wash thrips from affected plants using a garden hose, encourage predatory mites and lacewings with companion planting, or spray with soap, eco-oil or neem oil.
.png)