How to Grow Kohlrabi Seeds
Grow Guide #2279
Family: Brassicaceae
Binomial name: Brassica oleracea var. gongylodes
Life Cycle: Biennial (usually grown as an annual)
This 'How to Grow' guide details everything a home gardener needs to know to plant, grow and care for Kohlrabi (Brassica oleracea var. gongylodes).
When to Sow Kohlrabi Seeds
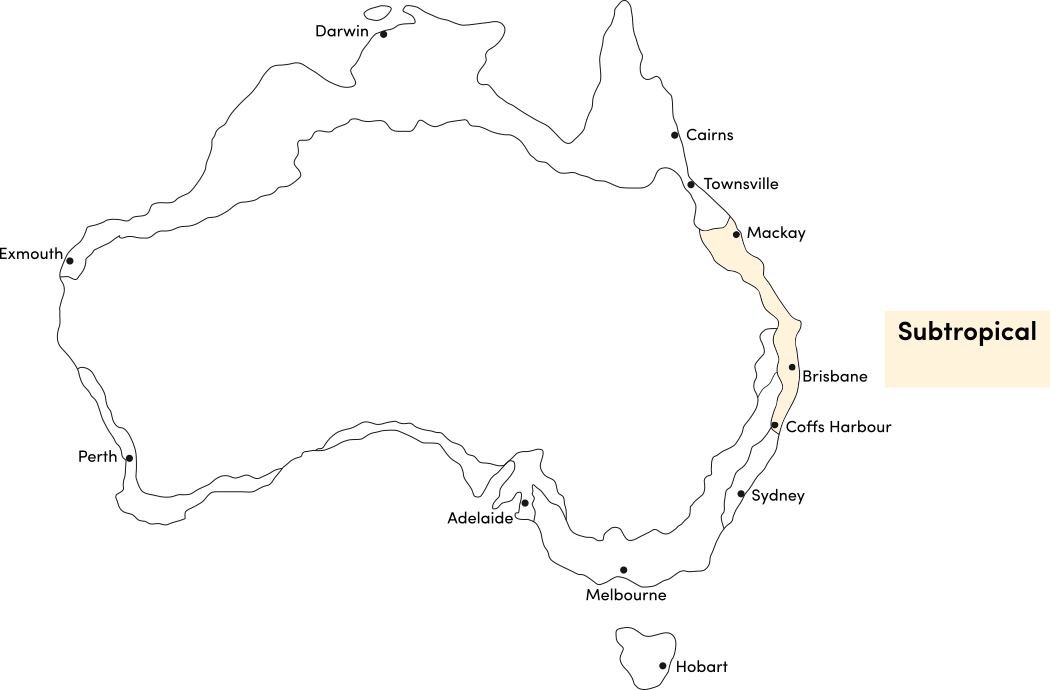
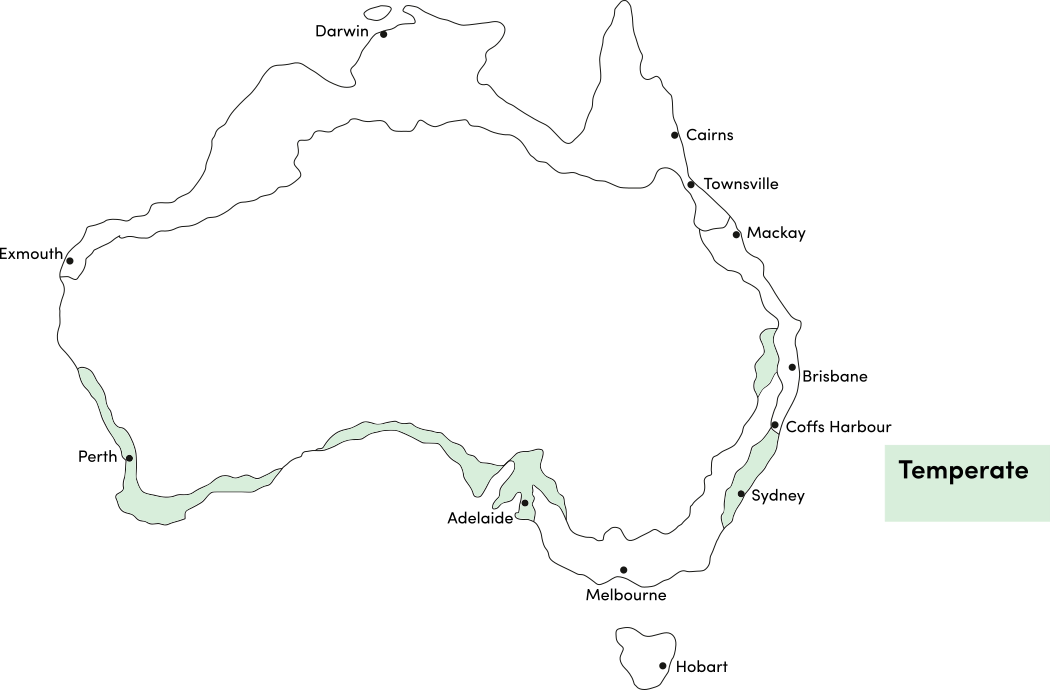
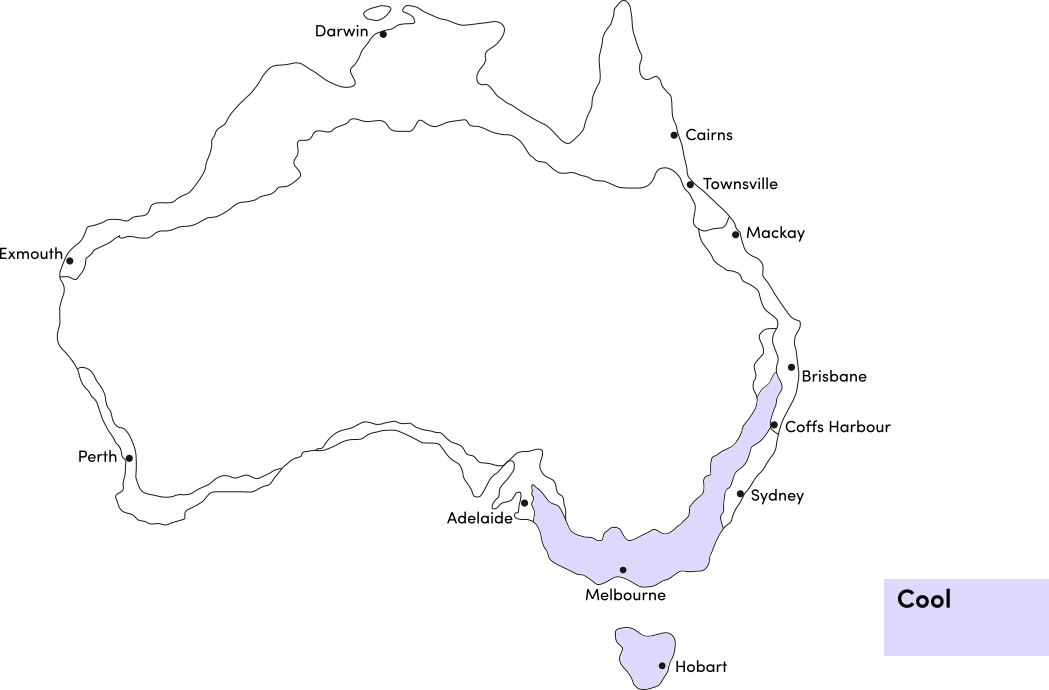
Kohlrabi can be grown year-round in most climates. Avoid planting in extremely hot or cold weather which can affect germination and growth. Use the table below to identify the best time of year to sow kohlrabi in your climate.
| JAN | FEB | MAR | APR | MAY | JUN | JUL | AUG | SEP | OCT | NOV | DEC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cool | ||||||||||||
| Temperate | ||||||||||||
| Sub-Tropical | ||||||||||||
| Tropical | ||||||||||||
| Arid |
Preparation
Kohlrabi plants are best grown in full sun or part shade. Choose a location that will receive at least 3 hours of full sun each day.
Kohlrabi plants need a well drained soil enriched with plenty of organic matter. Prepare soil by weeding it thoroughly, digging it over to loosen it and adding aged animal manure or compost. Keep the area free of weeds until planting. Learn more about preparing soil for planting here.
Kohlrabi plants can be grown in containers. If possible choose a variety that’s recommended for container growing. Use a good quality potting mix and make sure your container is large enough for mature plants; a minimum of 40 litres is recommended for kohlrabi. During the growing season, keep in mind that container grown plants may need additional fertiliser to encourage healthy growth.
How to Sow Kohlrabi Seeds
Kohlrabi seeds do not require any treatment (eg soaking, stratification) before sowing.
Kohlrabi seeds grow best when they are sown directly into the garden.
- Sow seeds directly in the garden 5mm deep and 10-20cm apart, with rows 30-40cm apart.
- Keep soil moist but never wet or dry.
- Seeds should germinate in around 3-10 days at a soil temperature of 16-27°C.
- Young seedlings will need protection from pests, pets and weather until they are established.
How to Grow Kohlrabi
Kohlrabi plants may need watering during the growing season. Water when the soil is dry about 5cm below the surface (test this by scratching away a little soil with your finger). Water deeply in the early morning or late afternoon. Avoid watering the leaves of plants to avoid fungal diseases. Learn more about watering here.
If soil was well prepared no extra fertiliser should be necessary. In poor soil or to give your plants an extra boost, application of a balanced fertiliser or one formulated for fruit and vegetables can be beneficial:
- Apply slow release fertiliser at the recommended rate when transplanting or when seedlings are 5-10cm tall.
- Apply liquid fertiliser at the recommended rate and frequency while plants are fruiting or flowering.
How to Harvest Kohlrabi
Kohlrabi should be ready to harvest in approximately 55-70 days.
Leaves are ready to harvest when they are large enough to eat, and can be harvested as needed. Harvest leaves by pinching off the outer leaves, leaving some on the plant for future growth. Eat kohlrabi leaves as soon as possible after harvesting. Store leaves short term in a perforated plastic bag in the fridge.
Stems are ready to harvest when they are large enough to eat, and can be harvested as needed. Harvest individual stems by cutting them just above ground level. Cut the foliage 1-2cm above the top of the stem. Store kohlrabi in a perforated plastic bag in the fridge. For longer term storage, kohlrabi can be pickled or blanched and frozen.
Common Problems when Growing Kohlrabi
Like all plants, kohlrabi is susceptible to some pests, diseases and other problems. Below is a list of the most common problems gardeners encounter when growing kohlrabi plants:
 Cabbage moth and cabbage white butterfly have white or grey wings with distinctive markings. They lay their eggs on the underside of leaves. Their caterpillars feed on the leaves, creating large holes and sometimes skeletonising the leaves. Use netting to exclude butterflies and moths or decoys to deter them. Pick the caterpillars off the plants or use an appropriate spray in a selective and targeted way. Read more about cabbage moth and cabbage white butterfly here.
Cabbage moth and cabbage white butterfly have white or grey wings with distinctive markings. They lay their eggs on the underside of leaves. Their caterpillars feed on the leaves, creating large holes and sometimes skeletonising the leaves. Use netting to exclude butterflies and moths or decoys to deter them. Pick the caterpillars off the plants or use an appropriate spray in a selective and targeted way. Read more about cabbage moth and cabbage white butterfly here. Slugs and snails are molluscs that feed on tender leaves and shoots, mostly at night, leaving slimy trails behind them. Control them by removing their hiding places, keeping free range poultry, collecting them by torchlight or by placing traps. Read more about slugs and snails here.
Slugs and snails are molluscs that feed on tender leaves and shoots, mostly at night, leaving slimy trails behind them. Control them by removing their hiding places, keeping free range poultry, collecting them by torchlight or by placing traps. Read more about slugs and snails here. Aphids are small (2-4mm long) sap-sucking insects that congregate on the new shoots or the undersides of leaves. They can cause leaves to wilt or become discoloured, and also excrete honeydew which can attract ants and other insect pests. To manage aphids, remove them by spraying with a garden hose, apply a soap or alcohol spray, or encourage predatory insects to your garden. Read more about aphids here.
Aphids are small (2-4mm long) sap-sucking insects that congregate on the new shoots or the undersides of leaves. They can cause leaves to wilt or become discoloured, and also excrete honeydew which can attract ants and other insect pests. To manage aphids, remove them by spraying with a garden hose, apply a soap or alcohol spray, or encourage predatory insects to your garden. Read more about aphids here. Bolting is when a plant prematurely flowers and goes to seed. Bolting can be caused by a period of extreme weather. Avoid sowing seed until after the danger of frosts has passed or in very hot weather. Water plants regularly and deeply in hot weather to prevent them suffering heat stress.
Bolting is when a plant prematurely flowers and goes to seed. Bolting can be caused by a period of extreme weather. Avoid sowing seed until after the danger of frosts has passed or in very hot weather. Water plants regularly and deeply in hot weather to prevent them suffering heat stress. Tough stems can indicate that the crop was grown too slowly, that plants were heat or water stressed, or that stems were harvested too late. Provide adequate water and nutrients to grow the crop quickly. Do not grow crops in extreme heat or cold. Harvest stems when they are young and tender.
Tough stems can indicate that the crop was grown too slowly, that plants were heat or water stressed, or that stems were harvested too late. Provide adequate water and nutrients to grow the crop quickly. Do not grow crops in extreme heat or cold. Harvest stems when they are young and tender. Stem not swollen can be the result of sowing seed too thickly, growing plants too slowly, or water or heat stress. Thin seedlings to give plants adequate space to grow. Provide adequate water and nutrients to grow the crop quickly. Do not grow crops in extreme heat or cold.
Stem not swollen can be the result of sowing seed too thickly, growing plants too slowly, or water or heat stress. Thin seedlings to give plants adequate space to grow. Provide adequate water and nutrients to grow the crop quickly. Do not grow crops in extreme heat or cold.
.png)