How do you describe a flower? Lush depictions of colour and scent may be great for poetry, but they're a little less accurate when it comes to seed packets or wildflower field guides.
To have a good idea of how a seed's mature plant will look, or to identify an unknown flower you've stumbled across, it helps to understand the more technical ways of describing them. Here are the basics you need to know.
1) Flower Shapes
Individual flowers come in a variety of shapes, divided into two broad types. With the first, the overall flower shape is rounded and symmetrical. With the second, the flowers form a more tube-like shape, and the petals may be positioned irregularly on the stalk.
Within those two types there are a variety of common shapes.
- Cross-Shaped (cruciform): Consisting of four individual petals, one for each point of the compass.
- Star-Shaped (stellate): With distinct individual petals radiating outward from the centre.
- Saucer-Shaped: Larger, broader petals growing close together to form a shallow bowl.
- Cup-Shaped: A deeper version of the saucer shape.
- Bell-Shaped (campanulate): An even deeper, narrower bowl, with the petals splaying outward as they reach their tips.
- Tubular: Like a bell-shaped flower that's closed in on itself to form a long, tight tube.
- Funnel-Shaped: A less-tightly packed version of the tubular shape, with the petals fanning slightly outward.
- Pitcher-Shaped: With a wide, rounded bottom of the flower tapering in toward the top to form a cone shape.
- Trumpet-Shaped: A tight funnel at the bottom, with the petals opening gently out from halfway to resemble the musical instrument.
- Salverform: A more extreme version of the trumpet, where the petals spread out at right angles from halfway up to give an open, round-faced display.
- Rosette: Consists of several rows of tightly packed flowers, arranged in whorls or circles.
- Pompom: A rosette shape taken to extremes, with the rows curling backward to form a dome or ball.
- Pea-Like: An unsymmetrical shape, with a single large upper petal, two medium side ones, and either two small petals or a fused pair at the bottom.
- Slipper-Shaped: An irregular shape with long petals forming a pouch.
2) Petal Arrangements
In general, wildflowers tend to have the most basic petal arrangements, and as you move up the cultivation levels they become more complex and ornamental. The arrangements are described in six main ways.
- Single: The simplest petal layout, with a single row of relatively flat petals.
- Recurved petals: The petals curve backwards and upwards from the central point, exposing the stamens prominently.
- Reflexed petals: Similar to recurved, but with straighter petals pointing slightly or strongly backward.
- Semi-Double: Two or three rows of petals, forming a typical rose shape.
- Double: Several rows of petals forming a tight, multi-layered circle, with few or no visible stamens.
- Fully Double: A dense dome or ball of petals, often with no visible stamens at all.
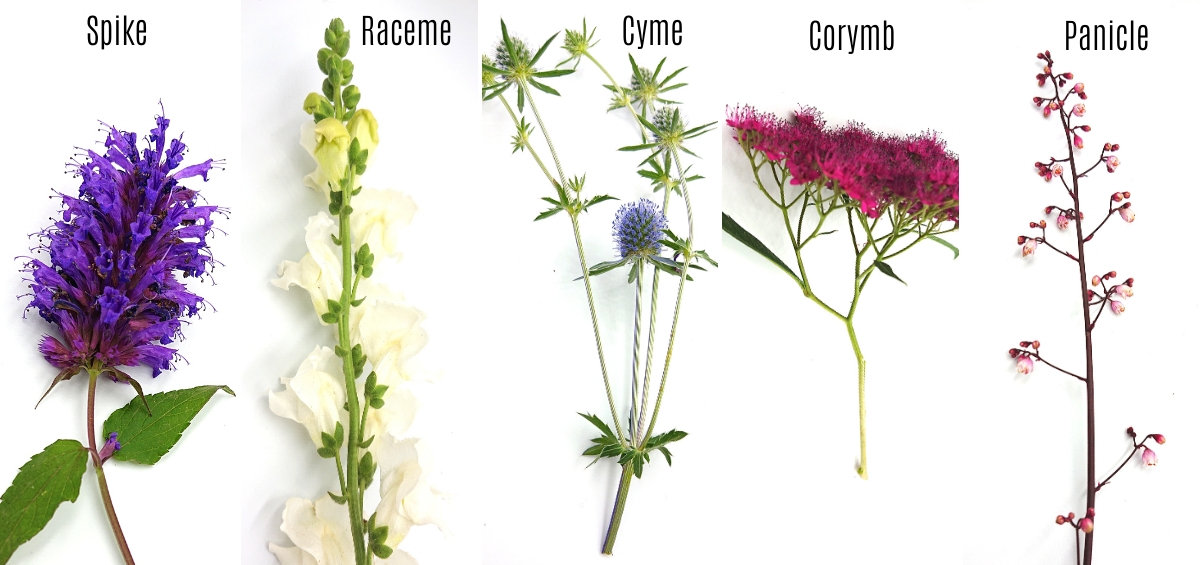
3) Flower Inflorescence
However, not all plants produce a single flower on a single stem. The way that flowers are grouped together is known as an inflorescence, and there are many types.
- Solitary: Each flower on the plant is a single flower on a single stalk.
- Cluster: Multiple flowers each with an unbranched stalk, all originating from the same point on the stem.
- Umbel: Similar to a cluster, but with the multiple flowers forming a bowl-like radiated shape. All the stalks radiate from a single point on the tip of the stem.
- Flowerhead: Many miniature, stalkless florets packed across a flattened disc or pad.
- Raceme: A single main stem, sprouting multiple side-stalks each with a single flower.
- Cyme: Each stem contains multiple side-stalks with several flowers each.
- Spike: Many stalkless flowers radiating outward around a single stem, usually growing very densely.
- Corymb: A dense cluster of single-flowered stalks growing from different parts of the main stem, and coming together to form a dome or flat-topped cluster that often resembles a single flower.
- Panicle: The most complex arrangement of flowers, with several sets of raceme, cyme or corymb clusters branching off from a central stem.
4) Flower Habits
The habit of a flower is simply the way it hangs from its stalk, whether it's a single flower or one of a group. It's important to note that the habit often changes as the flower develops, and so for consistency species are usually described using their mature habit.
- Erect: All the petals and other flower parts point straight upward.
- Horizontal: The flower points sideways at a right angle from the stem.
- Nodding: Pointing loosely downward from an upright stem which bends down under the weight.
- Pendent: The entire flower hangs vertically downward from a horizontal or downward-pointing stem.
5) Flower Colour Types
Lastly, although flowers have a huge range of actual hues, their colour types and patterns can be split into four general groups.
- Self-Coloured: A basic single colour, uniform across the petals.
- Bicoloured: As the names suggests, containing two distinct colours in the same petal, with a clear dividing line somewhere between the base and the tip. More common in highly cultivated ornamentals, although it can happen spontaneously with many species.
- Picotee: A variant of the bicoloured type, where the edge of the petal is a different colour to the rest of it, again with a sharp dividing line rather than a gradual change.
- Striped: Flowers containing two colours arranged in stripes along the length of the petal.
Even the simplest flower can have its own beauty, but as they become more complex it gets ever more difficult to describe their features. While these technical terms might not be common in everyday language, putting them together lets you accurately describe almost any flower, whether it's totally wild or painstakingly cultivated.
photos by Nat Buttenshaw